PhD Summary
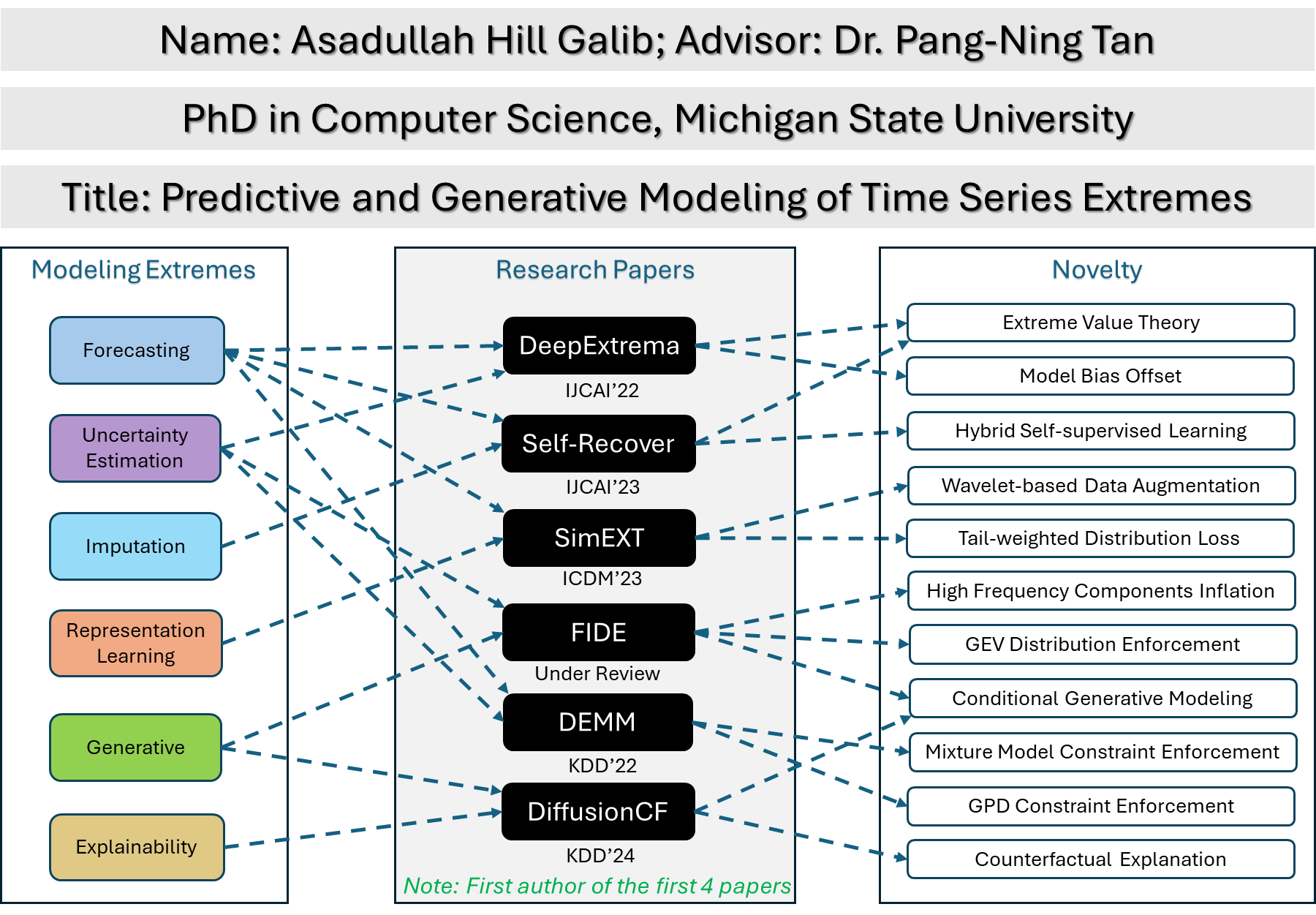
Dissertation Title: Predictive and Generative Modeling of Time Series Extremes
Advisor: Dr. Pang-Ning Tan
Abstract:
The accurate modeling of extreme values in time series data is a critical yet challenging task that has garnered significant interest in recent years. The impact of extreme events on human and natural systems underscores the need for effective and reliable modeling methods. The proposed thesis aims to develop novel deep learning frameworks that can effectively model extreme events in time series data. The thesis introduces four novel deep learning frameworks: DeepExtrema, Self-Recover, SimEXT, and FIDE, which offer promising solutions for forecasting, imputation, representation learning, and generative modeling of extreme values in time series data. DeepExtrema focuses on integrating extreme value theory with deep learning formulation to improve the accuracy and reliability of extreme events forecasting. Self-Recover addresses data fusion challenges that arise from varying temporal coverage associated with long-term and random missing values of predictors. SimEXT explores how deep learning can be utilized to learn useful time series representations that effectively capture tail distributions for modeling extreme events. FIDE introduces a high-frequency inflation-based conditional diffusion model tailored towards preserving extreme value distributions within generative modeling. These frameworks are evaluated using real-world and synthetic datasets, demonstrating superior performance over existing state-of-the-art methods. The contributions of this research are significant in advancing the field of time series modeling and have practical implications across various domains, such as climate science, finance, and engineering.
Publications:
- Galib, A. H., McDonald, A., Wilson, T., Luo, L., & Tan, P. N. (2022, Jul.). DeepExtrema: A Deep Learning Approach for Forecasting Block Maxima in Time Series Data. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2022 (pp. 2980-2986). PDF
- Galib, A. H., McDonald, A., Tan, P. N. & Luo, L. (2023, Aug.). Self-Recover: Forecasting Block Maxima in Time Series from Predictors with Disparate Temporal Coverage using Self-Supervised Learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2023 (pp. 3723-3731). PDF
- Galib, A. H., Tan, P. N. & Luo, L. (2023, Dec.). SimEXT: Self-supervised Representation Learning for Extreme Values in Time Series. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM 2023 (pp. 1031-1036), IEEE. PDF
- Galib, A. H., Tan, P. N. & Luo, L. (2024, May.). FIDE: Frequency-Inflated Conditional Diffusion Model for Extreme-Aware Time Series Generation. [Under Review].
- Deng, Y., Galib, A. H., Tan, P. N., & Luo, L. (2024, Aug.). Unraveling Block Maxima Forecasting Models with Counterfactual Explanation. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD 2024 Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2024.
- Wilson, T., McDonald, A., Galib, A. H., Luo, L., & Tan, P. N. (2022, Aug.). Beyond Point Prediction: Capturing Zero-Inflated \& Heavy-Tailed Spatiotemporal Data with Deep Extreme Mixture Models. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD 2022 Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD 2022 (pp. 2020-2028). PDF
- Wilson, T., Tan P., Luo, L., & Galib, A. H. (2021, Dec.). Deep Learning With Extreme Value Theory for Modeling Precipitation Events. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts (Vol. 2021, pp. A15Q-07).
